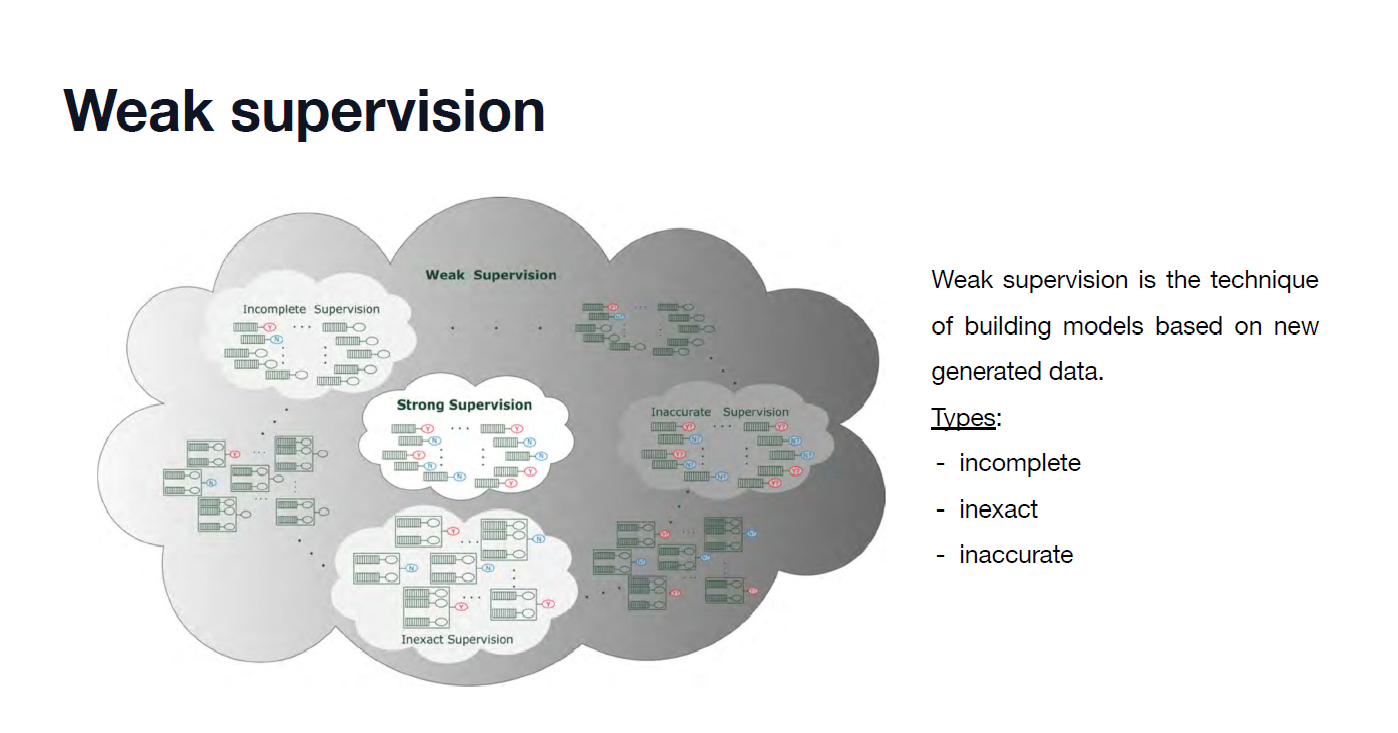
LeNet 신경망 - MiniPlaces 이미지 분류
LeNet 신경망을 활용해서 MiniPlaces 데이터셋 이미지 분류 작업을 수행한다.
‘MiniPlaces’ 데이터셋은 캐글과 같은 온라인에서 손쉽게 구할 수 있다 여기.
Code
[Notice] download here
CNN이나 LeNet 신경망에 대한 보다 자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하자.
라이브러리 불러오기
# python imports
import os
from tqdm import tqdm
# torch imports
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
# helper functions for computer vision
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
LeNet 신경망 구축
class LeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_shape=(32, 32), num_classes=100):
super(LeNet, self).__init__()
# certain definitions
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3,6,5,1,0)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6,16,5,1,0)
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(400,256)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(256,128)
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(128, num_classes)
# 순전파
def forward(self, x):
shape_dict = {}
# certain operations
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), 2,2,0)
shape_dict[1] = x.shape
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2,2,0)
shape_dict[2] = x.shape
x = self.flatten(x)
shape_dict[3] = x.shape
x = F.relu(self.linear1(x))
shape_dict[4] = x.shape
x = F.relu(self.linear2(x))
shape_dict[5] = x.shape
x = self.linear3(x)
shape_dict[6] = x.shape
out = x
return out, shape_dict
상기 LeNet 신경망에서 초기값 및 순전파 과정을 정의한다.
PyTorch 특성상 이후 학습 단계에서 역전파를 정의할 예정이다.
‘Stride, Pooling, Padding’ 혹은 순/역전파에 관한 보다 자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하자.
학습 가능 피라미터 개수(Optional)
def count_model_params():
'''
return the number of trainable parameters of LeNet.
'''
model = LeNet()
model_params = 0.0
model_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
return model_params / 1e6
해당 과정은 학습에 필수는 아니지만, 교육 측면에서 도움이 될 수 있으니 만들어보았다.
모델 학습
하기 코드 옆에 주석을 자세히 달아놨으니 참조하며 읽어보길 바란다.
def train_model(model, train_loader, optimizer, criterion, epoch):
"""
model (torch.nn.module): The model created to train
train_loader (pytorch data loader): Training data loader
optimizer (optimizer.*): A instance of some sort of optimizer, usually SGD
criterion (nn.CrossEntropyLoss) : Loss function used to train the network
epoch (int): Current epoch number
"""
model.train()
train_loss = 0.0
for input, target in tqdm(train_loader, total=len(train_loader)):
###################################
# fill in the standard training loop of forward pass,
# backward pass, loss computation and optimizer step
###################################
# 1) zero the parameter gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 2) forward + backward + optimize
output, _ = model(input)
loss = criterion(output, target)
loss.backward() # 역전파 진행
optimizer.step()
# Update the train_loss variable
# .item() detaches the node from the computational graph
# Uncomment the below line after you fill block 1 and 2
train_loss += loss.item()
train_loss /= len(train_loader)
print('[Training set] Epoch: {:d}, Average loss: {:.4f}'.format(epoch+1, train_loss))
return train_loss
‘tqdm‘는 progress bar를 생성해주고, 함수나 반복문의 TTC (Time To Completion) 를 예측하는 파이썬 패키지이다.
모델 학습 과정을 실시간으로 확인하기 위해 불러온 패키지이다.
주요 특징들을 살펴보자:
- optimizer.zero_grad(): 이전 step에서 각 layer 별로 계산된 gradient 값을 모두 0으로 초기화 시키는 작업으로, 0으로 초기화 하지 않으면 이전 step의 결과에 현재 step의 gradient가 누적으로 합해져서 계산된다.
- criterion: 손실함수 (이 프로젝트는 ‘크로스 엔트로피‘를 활용한다)
- optimizer: 최적화 방법 (i.e., Adam)
- loss.backward(): back-propagation을 통해 gradient를 계산한다.
- optimizer.step(): 각 layer의 gradient 값을 이용하여 파라미터를 업데이트.
- train_loss += loss.item(): 손실값 누적 계산
크로스 엔트로피(Cross Entropy)에 관한 보다 자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하자.
보다 자세한 PyTorch 문법은 외부 사이트 여기를 참조하길 바란다.
모델 테스트
def test_model(model, test_loader, epoch):
model.eval()
correct = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for input, target in test_loader:
output, _ = model(input)
pred = output.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
test_acc = correct / len(test_loader.dataset)
print('[Test set] Epoch: {:d}, Accuracy: {:.2f}%\n'.format(
epoch+1, 100. * test_acc))
return test_acc
이제 개인적으로 각자 MiniPlaces 데이터셋을 활용해서 직접 PyTorch로 모델을 학습시켜보도록 하자.




댓글남기기