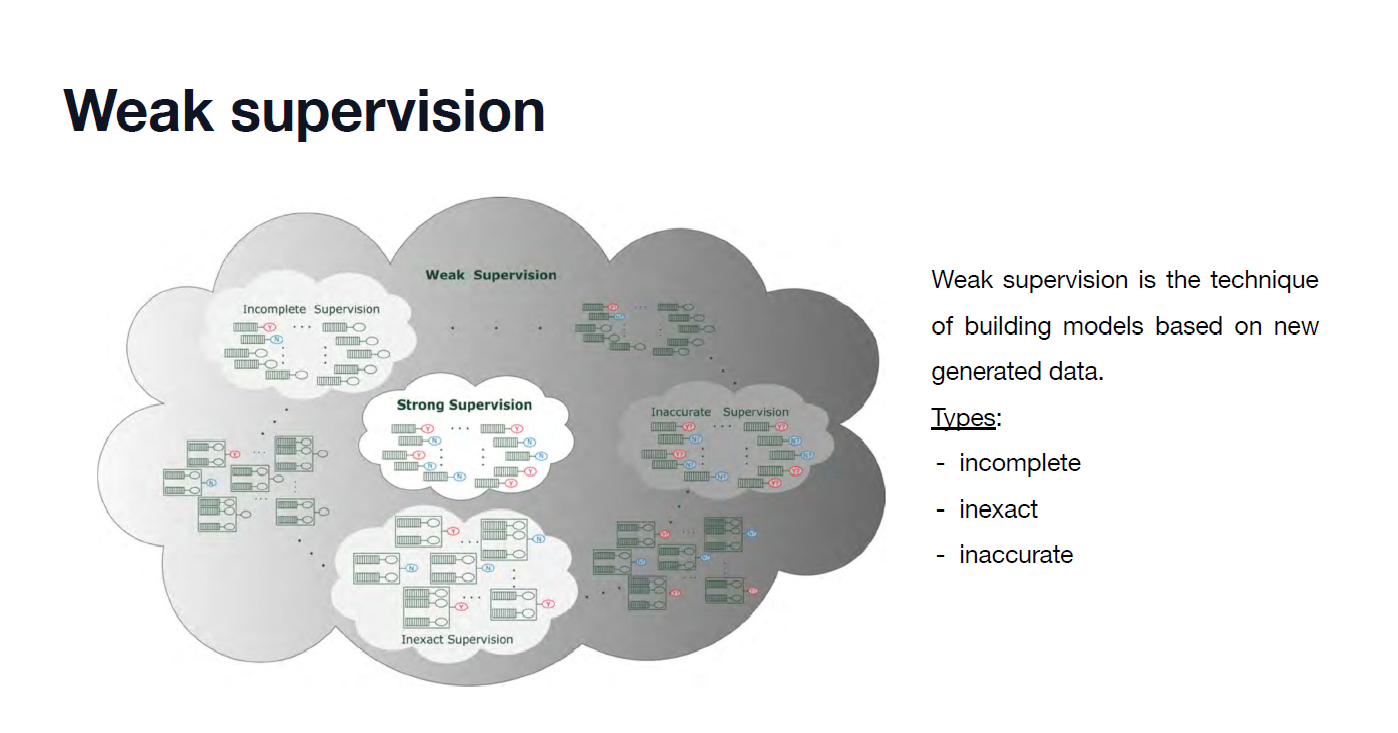
[논문분석] Entropy regularization for weakly supervised object localization (PRL 2023)
논문링크 .
한줄요약 ✔
- The objective of classification training is not entirely consistent with that of localization.
- Very low entropy might be important for classification, but less helpful for localization.
- Sweet spot for localization with respect to entropy.
- new term to the loss function.
- predicted class prob. vector가 uniform dist.에 닮게 만드는 정도를 조절 → uniform dist.는 각 클래스 예측 확률이 동일 (class 예측 불확실성 증가) → localization 성능 증가.
- new term to the loss function.
Preliminaries 🍱
Weakly-supervised object localization (WSOL)
- The goal of weakly-supervised object localization (WSOL) is to train a localization model without the location information of the object.
- Object localization requires expensive pixel-level annotations (e.g., bounding boxes or segmentation masks).
- A well-known limitation of WSOL methods is that the model only focuses on the most discriminative part, which hinders capturing the entire extent of the object accurately.
- The model captures not only the target object but also frequently co-occurring background components (e.g., snowboard-snow, train-railroad).
- The mainstream of WSOL is to train a CNN-based image classification model and then extract an attention map using a visual interpretable method (i.e., CAM, Grad-CAM, etc.).
Regularization
\(\mathcal{L}(\theta):=(1-\gamma)\mathbf{H}(y,p_{\theta})-\gamma \mathbf{KL}(u \vert\vert p_{\theta})\)
Label smoothing (CVPR’15)
- To avoid overfitting (i.e., Dropout, L2, data aug., etc.).
- Introduces noise to the ground truth labels.
- 상기 그림에서 target dist.(GT)가 soft labels처럼 변경되어 entropy가 증가한 모습이다. 이는 모델의 예측 분포가 서로 다른 클래스에 미량의 확률을 부여할 수 있기에 GT인 이 soft labels분포와 더 유사해질 수 있어서 모델 예측 결과인 output dist. 의 entropy는 더 낮다.
Confidence penalty (ICLR’17)
\(\mathcal{L}(\theta)=\mathbf{H}(y,p_{\theta})-\lambda \mathbf{H}(p_{\theta})\)
\[=\mathbf{H}(y,p_{\theta})-\lambda \mathbf{KL}(p_{\theta} \vert \vert u)\] \[=\mathbf{H}(y,p_{\theta})-\lambda \mathbf{JSD}(p_{\theta} \vert \vert u)\]Jensen Shannon (JS) divergence
\(\mathbf{JSD}(p_{\theta} \vert \vert u) = \mathbf{KL}(u \vert \vert p_{\theta}) + \mathbf{KL}(p_{\theta} \vert \vert u)\)
- 두 확률 분포 사이의 차이를 측정하는 통계적인 방법 중 하나.
JSD는 두 분포 간의 유사성을 나타내는 값으로, 쿨백-라이블러 발산(Kullback-Leibler Divergence)의 제곱근.
CAM
- a visual interpretable method that extracts an attention map from a classification network.
- computed as a channel-wise weighted average of the last convolutional feature map and the weights to the predicted class in the last fully connected layer.
Others
Hide-and-Seek (HaS, ICCV’17)
- 정의
- a data augmentation that divides the images into rectangular patches and then hides the randomly selected patches during training.
- 직접 가림.
- 목적
- the classification network might no longer see the most discriminative parts of the object, hence it can learn the less discriminative parts of the object as well.
CutMix (ICCV’19)
- 정의
- a data augmentation technique that cuts and pastes a patch from an image into another image and blends the target labels according to the size of the patch.
- target object에 다른 이미지에서 가져온 random patch를 덮어씌움.
- 목적
- CutMix is known to improve WSOL performance, since the classification network can learn the non-discriminative parts of objects.
Attention-based Dropout Layer (ADL, PAMI’21)
- 정의
- utilizes a self-attention mechanism to find the most discriminative part of the object during training.
- attached to each layer of the classification network, which hides or boosts the most discriminative part.
- utilizes a self-attention mechanism to find the most discriminative part of the object during training.
- Remark
- non-discriminative parts 걸러낸다는 명목에서 Dropout 별칭 사용.
Region-based Dropout Layer with Attention Prior (RDAP, PR’21)
- 정의
- utilizes the self-attention mechanism to find the most discriminative part.
- unlike the ADL, RDAP hides the most discriminative part with a fixed-size square mask, which results in a more effective and robust improvement in WSOL.
- most discriminative parts를 가리고 학습하면서 전체 객체의 특성을 포함하는 상대적으로 less discriminative 부분에 대한 학습을 유도합니다.
- 간단한 예시로 설명하면, 만약 개를 분류하는 분류기가 얼굴 부분에 주로 주목했다면, AE를 사용하여 얼굴 부분을 지운다면 분류기는 다른 부분에 주목하게 됩니다. 이런식으로 모델은 물체의 다양한 특성을 고려하여 학습하게 되며, 이는 WSOL에서 전체 물체를 고려한 더 나은 지역화 성능으로 이어질 수 있습니다.
- most discriminative parts를 가리고 학습하면서 전체 객체의 특성을 포함하는 상대적으로 less discriminative 부분에 대한 학습을 유도합니다.
Cross Entropy
\(H(p,q)=-\Sigma p(x) log q(x)\)
- In general, classification networks are trained by minimizing cross-entropy \(H(p,q)\) between ground truth and predicted probability. That is, the entropy decreases as the training progresses, which improves classification accuracy.
- \(p\): the target distribution.
- \(q\): the approximation of the target distribution; prediction.
=> Very low entropy might be important for classification, but less helpful for localization.
=> The model with very high entropy (e.g., early stage in training) cannot produce informative CAM in terms of object location, which results in poor localization performance.
Challenges and Main Idea💣
C1) WSOL 모델 성능을 높이기 위해 Classification performance를 희생해야 한다 .
Idea) Entropy에 관해 regularization을 적용하여 localization과 classification 사이의 적절한 sweet point를 찾는다 .
Problem Definition ❤️
Given a WSOL model \(\mathcal{T}\).
Return a model \(\mathcal{S}\).
Such that \(\mathcal{S}\) outperforms \(\mathcal{T}\) in terms of both localization and classification.
Proposed Method 🧿
Loss Function
\(\mathcal{L}(\theta)=\mathbf{H}(y,p_{\theta})-\lambda \mathbf{KL}(u \Vert p_{\theta})\)
- \(u\): the uniform dist. vector.
- \(\lambda\): a hyperparameter that controls the intensity of regularization applied to the model during training.
- \(p_{\theta}\): predicted class probability.
- \(\mathbf{KL}(u \Vert p_{\theta})\): uniform distribution(\(u\)) 과 모델 예측(\(p\))이 비슷할수록 그 \(\mathbf{KL}\) 값은 감소하고, 이는 궁극적으로 \(\mathcal{L}\)를 감소시키는 방향으로 학습이 진행된다. 하여 해당 term을 loss func.에 추가함으로써 class 예측에 대한 모델의 entropy를 증가시키는 regularization을 통해 localization과 classification의 최적의 균형을 맞추는 최적의 sweet spot을 탐색한다.
- \(\mathbf{KL}(u \Vert p_{\theta})=\Sigma u log({u \over p_{\theta}})=\Sigma({1 \over C} log({1 \over C p_{\theta}}))=\Sigma({1 \over C} log({1 \over C})-log(p_{\theta}))\) .
- 상기 식에서, \(log({1 \over C})\)는 상수이므로 전체 항에서 제거 가능하여 아래 식이 최종적으로 도출된다.
- \(\mathbf{KL}(u \Vert p_{\theta})=\Sigma u log({u \over p_{\theta}})=-{1 \over C} \Sigma log(p_{\theta})\) .
- 마지막 \(-{1 \over C}\) 에서 음수 부호로 인해 Loss function에서 \(+ \lambda\) 로 부호가 조정되고, 이는 \(\mathbf{KL}\)가 감소할수록 모델 예측이 최대 entropy를 갖는 uniform dist.과 유사해지면서 classification perf.을 희생하여 더욱 다양한 클래스에 대하여 localization 예측을 유도한다.
- \(\mathbf{KL}(u \Vert p_{\theta})=\Sigma u log({u \over p_{\theta}})=\Sigma({1 \over C} log({1 \over C p_{\theta}}))=\Sigma({1 \over C} log({1 \over C})-log(p_{\theta}))\) .
Experiment 👀
Formulation
- Baseline: PreResNet-18 and SE-ResNet-50.
- Dataset: CUB and OpenImages.
- Implementation:
- Last strided convolution to non-strided convolution for doubling the resolution of the last convolutional layer.
- Inference phase:
- attention map 추출 with CAM.
- CUB 외 다른 dataset에서는 annotation masks(GT)가 제공되어 있어서 이 attnetion map을 evaluation에 직접 활용.
- 정답 레이블 추출 (mask annotations 제공하지 않는 CUB 같은 dataset만 해당):
- threshold the attention map with \(\sigma\) to obtain the object mask.
- highlighted 된 픽셀값들만 살리고 나머지는 0으로 만들어서 해당 객체 부분 attention만 강조하여 object mask 획득.
- obtain the tightest bounding box containing the largest connected contour in the predicted mask
- 가령, CUB dataset에서는 \(\sigma=0.15\)를 사용(이전 논문 결과 인용).
- threshold the attention map with \(\sigma\) to obtain the object mask.
- set \(\lambda=10^{-4}\) .
- attention map 추출 with CAM.
- Metrics:
- Top-1 localization acc. and GT-knownlocalization acc.
- Datasets:
- CUB (w/o mask annotations) \(\rightarrow\) \(IoU > 50%\).
- OpenImages, Oxford (w/ mask annotations) \(\rightarrow\) pixel-wise average precision (
PxAP). - PASCAL VOC 2012 (w/ mask annotations and multiple image classes) \(\rightarrow\)
mPxAPmetric.- average
PxAPof all classes.
- average
Quantitative Eval. Results
Comparison with other entropy regularization methods
Ablation
- Specifically, the highest performance is achieved with \(\lambda\) of \(10^{−4}\), where the performance gain is significant (86.8% of ours vs. 74.8% of previous SOTA).
- \(\lambda=10^{-3}\) 에서 OpenImages 성능 매우 안 좋은 이유?
- Training/Validation 단계에서 성능이 안좋음(underfitting) → CAM 모델이 poor localization 수행.
- 간단히 model selection으로 해결 가능 (\(\lambda=10^{-4}\)에서 최적의 결과).
⇒ it is important to induce the model to have an appropriate entropy for WSOL, and our method is effective in finding the high-performance point.
Relationship between performances and entropy
Comparison with Confidence penalty and label smoothing
Feature map visualization at each convolution layer
[Fig. 5. Qualitative evaluation results. We concatenate three images to show our results. The left side is the input image with a green prediction box and red ground truth box, the middle is the extracted attention map, and the right side is the overlap of the input image and the attention map.]
Open Reivew 💗
NA
Discussion 🍟
NA
Major Takeaways 😃
NA
Limitation
- 상기 사진에서처럼 보통 핸들과 앞문은 같이 위치해있는데, 본 논문의 모델은 이 두 개를 구분하지는 못한다.
- Without pixel-level annotation, it is not easy to obtain such information. Addressing this problem would be an interesting future research direction.
Conclusion ✨
NA
Reference
NA



댓글남기기