설명 가능한 AI (XAI): Saliency Map
Saliency Map은 하나의 이미지 샘플이 모델의 입력으로 들어가면, 그 샘플에 대한 예측 결과에 대한 설명을 이미지에서 중요한 부분에 하이라이트(heatmap)해서 보여준다.
Simple Gradient Method

입력에 대한 모델의 Gradient(가중치)로 설명을 제공한다.
여기서, Gradient는 딥러닝 모델 Back-Propagation 과정에서 간단히 구해지는 것이다.
- Gradient ↑ –> 해당 픽셀 중요도 ↑
장단점

장점
- Easy to compute (via back propagation)
단점
- Becomes noisy (due to shattering gradient)
- 조금씩 변화가 있는 같은 예측 결과값을 도출해내는 각 이미지들에 대한 설명은 다르게 나타날 수 있다.
Noise는 ‘SmoothGrad’로 해결 가능하다.
SmoothGrad

Noisy한 Gradient들을 많이 제거하고 평균적으로 남는 Gradient가 더 깨끗한 설명이 가능하다.
- Add some noise to the input and average!
- Averaging gradients of slightly perturbed input would smoothen the interpretation
- Typical heuristics
- Expectation is approximated with Monte Carlo (around 50 runs)
- 𝜎 is set to be 10~20% of 𝑥𝑚𝑎𝑥−𝑥𝑚𝑖𝑛
장단점

SmoothGrad seems to work better for uniform background
장점
- Clearer interpretation via simple averaging
- Applicable to most sensitive maps
‘SmoothGrad’는 Simple Gradient Method, 이후에 배울 Grad CAM 등 다양한 XAI 모델에 적용가능 한 기법이다!
단점
- Computationally expensive! (Back propagation 반복만큼 계산 수행)
Class Activation Map (CAM)
[Constraint of CAM]

- GAP: 픽셀 i,j에 대한 Activation(Kernel Map)들의 총합을 Activation 크기로 나눈 것이다.
- Y^c: 클래스 c에 대한 output 분류 score
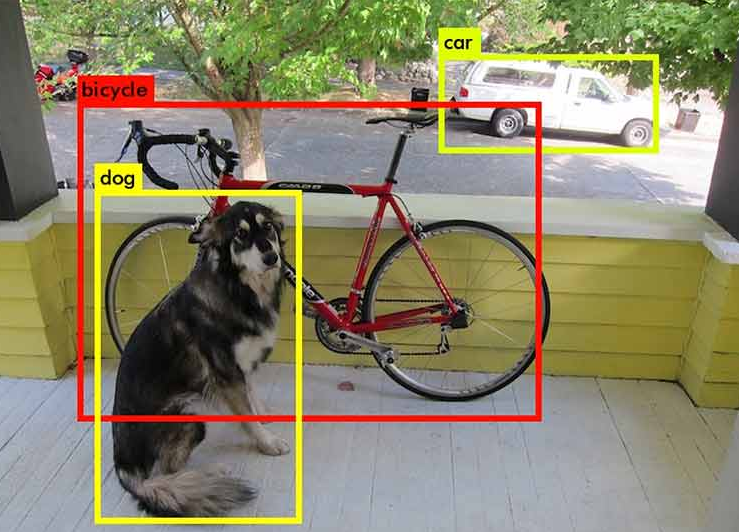
CAM이란 Saliency map 기반 설명 가능 방법으로, CNN이 입력으로 들어온 이미지를 분류할 때 “어떤 부분을 보고” 예측을 했는지를 알려주는 역할을 수행한다.
- CAM can localize objects in image.
- Segment the regions that have the value above 20% of the max value of the CAM and take the bounding box of it.
직관
CNN는 합성곱 연산을 통해 Kernel Maps를 생성하고, 이것들은 ‘Flatten’ 시킨 후 softmax 활성화 함수를 거쳐 ANN의 인풋으로 사용된다.
이 때, ‘Flatten’에서 이미지 특징을 포함하는 Kernel Maps 행렬 데이터를 1차원으로 재배열하기 때문에, 이미지 특성 각각에 대한 Localization 정보를 잃게된다.
차후 최종 출력에 히트맵으로써 이미지 특성이 드러나는 부분을 강조하면서 설명력을 제공하기 위하여, Kernel Maps의 localization 정보를 보존할 필요가 있다.


이를 위해, ‘Flatten’ 대신에 Global Average Pooling (GAP)이라는 특정 레이어를 만들고, 각각의 Kernel Maps의 localization 정보의 평균값을 1차원 배열의 형태로 변환한다.
- GAP의 목적은 feature를 1차원 벡터로 만들기 위함이다.
- GAP은 앞에서 설명한 Max Pooling 보다 더 급격하게 feature의 수를 줄인다.

각 Activation마다 하나의 숫자를 얻게되고, 그것들이 사진 속 동그라미들로써 표현된다.
그 숫자가 클수록 인풋과 연관성이 커서 결과 사진에서 보이는 바와같이 강조되어 표시된다.
활용 분야
- Object detection
- Semantic segmentation
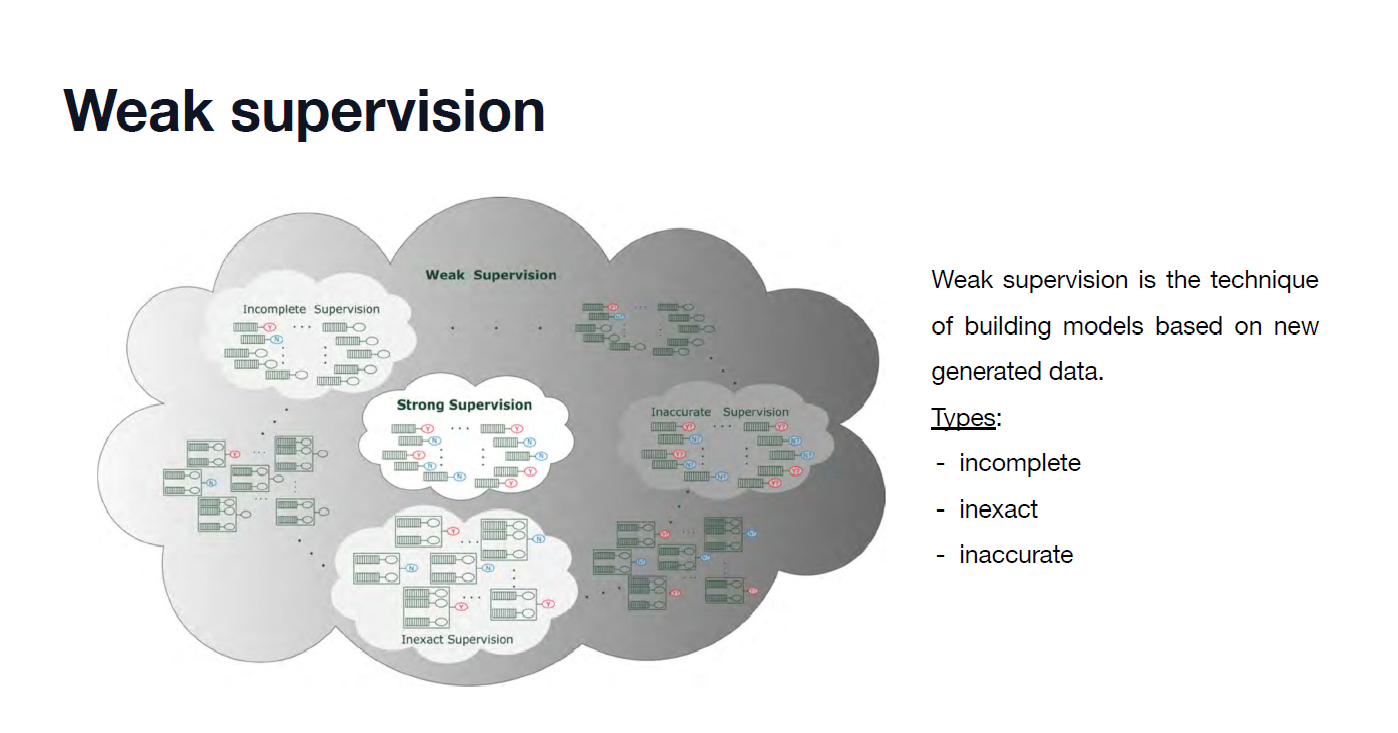
Weakly supervised learning
학습할 이미지에 대한 정보보다 예측해야할 정보가 더 디테일한 경우이다.
각 이미지마다 class label만 주어져 있어도 그것을 활용하여 분류기를 학습한 후, CAM 정보를 이용해서 더 복잡한 객체탐지 등과 같은 tasks들을 해결한다.
장단점
장점
- It clearly shows what objects the model is looking at
단점
- Model specific: it can be applied only to models with limited architecture (GAP이 적용된 Layer)
- It can only be obtained at the last convolutional layer, which makes the interpretation resolution coarse
- 객체의 boundary까지 정확하게 찾아내지는 못한다.
해결법: Grad-CAM
Grad-CAM

CAM을 Gradient 정보를 활용해서 확장한 설명 방법으로 GAP가 없어도 적용 가능하다.
CAM에서는 Feature Map에 GAP를 적용해 나온 가중치를 가지고 설명력을 표현했다.
상기 사진에서, Grad CAM은 Feature Map의 각 픽셀 값들(f_k(i, j))과 각 픽셀 별 가중치(a_k)를 곱하여 heatmap을 만든다.
이후, ‘pixel-wise sum’을 적용하고, ReLU 함수를 적용해 강조할 부분(= 출력의 근거가 되는 부분, 양의 가중치)을 골라낸 결과가 Grad CAM이다.
장단점

장점
- Model agnostic: can be applied to various output models
단점
- Average gradient sometimes is not accurate
- Gradient ↑ (절대적으로 옳은 중요도 X) –> 해당 Activation 출력 값 민감도 ↑
Reference
- Grad-CAM: 대선주자 얼굴 위치 추적기
- LG Aimers 교육 프로그램
이제, 본격적으로 다음 글에서 Perturbation-based 기법들에 대하여 학습해보자.




댓글남기기