A* Search - 8-tile Puzzle Game
Code
[Notice] download here

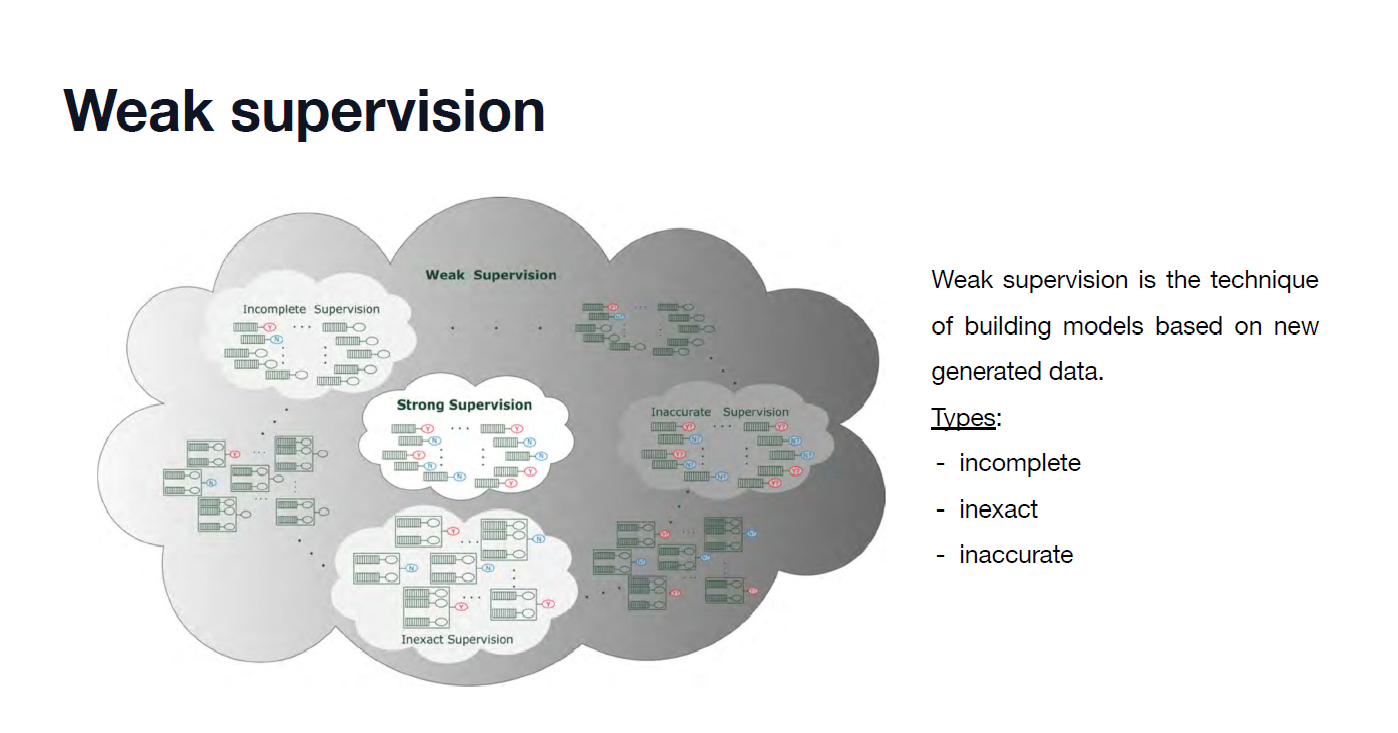
A-star 알고리즘을 활용해서 8-tile Puzzle 게임을 구현한다.
8-tile Puzzle 정보는 여기서 참고하자.
이 게임에서 당신은 AI 로봇과 Teeko 보드 게임을 펼치게 될 것이다.
A* 탐색 알고리즘은 시작 노드와 목적지 노드를 분명하게 지정해 이 두 노드 간의 최단 경로를 파악할 수 있다.
A* 알고리즘은 휴리스틱 추정값을 통해 알고리즘을 개선할 수 있다.
휴리스틱: 현재 step에서 destination까지의 최단 거리에 대한 비용값.
휴리스틱 추정값을 어떤 방식으로 제공하느냐에 따라 얼마나 빨리 최단 경로를 파악할 수 있느냐가 결정된다.
다익스트라 알고리즘: 시작 노드만을 지정해 다른 모든 노드에 대한 최단 경로를 파악한다.
import heapq # heap queue
게임 구현을 위해 필요한 라이브러리는 ‘heapq’ 밖에 없다.
Helper Functions
이제, 게임 동작에 필요한 헬퍼 함수들을 정의해보자.
- swap_item: 타일 이동
- state_to_dict: 현 state 정보를 ‘사전’으로 변경
- h_sum: 현 지점에서 목표가지의 최단 거리에 대한 비용값
- get_parent: 이전 step
- show_step: 진행 steps 보여주기
- contain: heapq 안에 해당 아이템 존재 여부
# 타일 이동
def swap_item(state, s1, s2):
tmp_s = state.copy()
t1 = tmp_s[s1]
tmp_s[s1] = state[s2]
tmp_s[s2] = t1
return tmp_s
# 상태를 '사전'으로 변환
def state_to_dict(states):
res = dict()
row = col = 0
for i in states:
if col > 2:
col = 0
row = row + 1
res[i] = [row, col]
col = col + 1
return res
# 목표까지의 최단 거리 비용값 계산
def h_sum(s, goal=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 0]):
s_dict = state_to_dict(s)
g_dict = state_to_dict(goal)
# skip zero index
s_dict[0] = [0, 0]
g_dict[0] = [0, 0]
# get heuristic sum
summ = 0
for k in s_dict:
summ += get_manhattan_distance(s_dict[k], g_dict[k])
return summ
# 이전 step 정보
def get_parent(dic, s):
for k, v in dic.items():
if v[0] == s:
return k
return -1
# 현 진행 step 현황 표시
def show_step(t_dic, goal = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 0]):
steps = []
p_idx = -1
# get parent
for k, v in t_dic.items():
if v[0] == goal:
p_idx = k
# track
while p_idx != -1:
steps.append(t_dic[p_idx][0])
p_idx = t_dic[p_idx][1]
# print steps
moves = 0
for i in steps[::-1]:
print("{} h={} moves: {}".format(i, h_sum(i, goal), moves))
moves += 1
# 힙큐에 해당 아이템 존재 여부
def contain(pq, s):
for idx in pq:
if idx[1] == s:
return True
return False
Required Functions
이제, 게임 동작에 필요한 헬퍼 함수들을 정의해보자.
- get_manhattan_distance: states 간 Manhattan distance 도출
- print_succ: Prints the list of all the valid successors in the puzzle.
- get_succ: valid한 다음 목표 지점을 불러온다
- solve: Implement the A* algorithm here.
def get_manhattan_distance(from_state, to_state=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 0]):
"""
TODO: implement this function. This function will not be tested directly by the grader.
INPUT:
Two states (if second state is omitted then it is assumed that it is the goal state)
RETURNS:
A scalar that is the sum of Manhattan distances for all tiles.
"""
return abs(from_state[0] - to_state[0]) + abs(from_state[1] - to_state[1])
def print_succ(state):
"""
TODO: This is based on get_succ function below, so should implement that function.
INPUT:
A state (list of length 9)
WHAT IT DOES:
Prints the list of all the valid successors in the puzzle.
"""
succ_states = get_succ(state)
for succ_state in succ_states:
print(succ_state, "h={}".format(h_sum(succ_state)))
def get_succ(state):
"""
TODO: implement this function.
INPUT:
A state (list of length 9)
RETURNS:
A list of all the valid successors in the puzzle (don't forget to sort the result as done below).
"""
zeros = list(filter(lambda x: state[x] == 0, range(len(state))))
succ_states = []
for zero_idx in zeros:
if zero_idx == 4: # cetner
if state[1] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 1, 4))
if state[3] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 3, 4))
if state[5] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 5, 4))
if state[7] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 7, 4))
elif zero_idx % 2 == 0: # corner
if zero_idx == 0:
if state[1] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 0, 1))
if state[3] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 0, 3))
if zero_idx == 2:
if state[1] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 2, 1))
if state[5] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 2, 5))
if zero_idx == 6:
if state[3] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 6, 3))
if state[7] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 6, 7))
if zero_idx == 8:
if state[7] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 8, 7))
if state[5] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 8, 5))
else: # middle of boundary
if zero_idx == 1:
if state[0] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 1, 0))
if state[2] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 1, 2))
if state[4] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 1, 4))
if zero_idx == 3:
if state[0] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 3, 0))
if state[4] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 3, 4))
if state[6] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 3, 6))
if zero_idx == 5:
if state[2] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 5, 2))
if state[4] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 5, 4))
if state[8] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 5, 8))
if zero_idx == 7:
if state[4] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 7, 4))
if state[6] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 7, 6))
if state[8] != 0:
succ_states.append(swap_item(state, 7, 8))
return sorted(succ_states)
def solve(state, goal_state=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 0]):
"""
TODO: Implement the A* algorithm here.
INPUT:
An initial state (list of length 9)
WHAT IT SHOULD DO:
Prints a path of configurations from initial state to goal state along h values, number of moves, and max queue number in the format specified in the pdf.
"""
pq = []
heapq.heappush(pq, (0 + h_sum(state, goal_state), state, (0, h_sum(state, goal_state), -1)))
track_dic = {0: [state, -1]}
visited = []
curr_idx = 1
max_len = 0
while True:
popped = heapq.heappop(pq)
popped_s = popped[1]
# end
if popped_s == goal_state:
show_step(track_dic, goal_state)
print("Max queue length: {}".format(max_len))
break
popped_i = popped[2]
if popped_s not in visited:
visited.append(popped_s)
p_idx = get_parent(track_dic, popped_s)
succ_states = get_succ(popped_s)
for succ_state in succ_states:
if succ_state not in visited and not contain(pq, succ_state):
g = popped_i[0] + 1
h = h_sum(succ_state, goal_state)
heapq.heappush(pq, (g + h, succ_state, (g, h, popped_i[2] + 1)))
if len(pq) > max_len:
max_len = len(pq)
track_dic[curr_idx] = [succ_state, p_idx]
curr_idx += 1
상기 solve 함수에서 주목해야할 부분은 heapq.heappush(pq, (g + h, succ_state, (g, h, popped_i[2] + 1))) 이 부분이다.
‘heapq.heappush(pq ,(cost, state, (g, h, parent_index)))’
- pq: the priority queue
- g: the cost from the starting node (= the number of moves so far): 초기 ~ 현재 step
- h: the value of the heuristic function: 현재 step ~ 목표
- cost=g+h
- A parent index: 이전 step의 index; -1 denotes the initial state(without any parent).
결과
자, 이제 게임 실행을 위해 필요한 모든 세팅은 끝이났다.
test = [4,3,0,5,1,6,7,2,0]
print_succ(test)
print()
print(get_manhattan_distance(test, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 0]))
print()
solve(test)
print()

초기 타일 배치를 [4,3,0,5,1,6,7,2,0]라 했을 때, 상기 이미지처럼 목표 타일 배치를 [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,0,0]라 설정하자.
A* 탐색 알고리즘에 기반하여 시스템이 알아서 최대 효율로 초기 타일 배치를 목표 타일 배치로 변경시킬 것이다.
아래가 그 결과이다.

‘h’는 휴리스틱 추정값으로, 목표 배치 타일까지 필요한 최소 타일 이동 횟수를 나타낸다.
- 궁극적으로, 마지막에 목표 타일 배치에 도달하면 이동시킬 타일이 없어서 ‘h=0’이 될 것이다.
가장 아래 ‘Max queue length’는 우리가 구현한 heapq 안에 저장되어 있던 목표에 도달하기 위해 필요한 모든 경로에 대해 저장된 정보의 최대 개수이다.
- 근본적으로, 메모리를 많이 할당하지 않기 위해, 그 값이 작을수록 시스템 디버깅에 부담이 적을 것이다.




댓글남기기