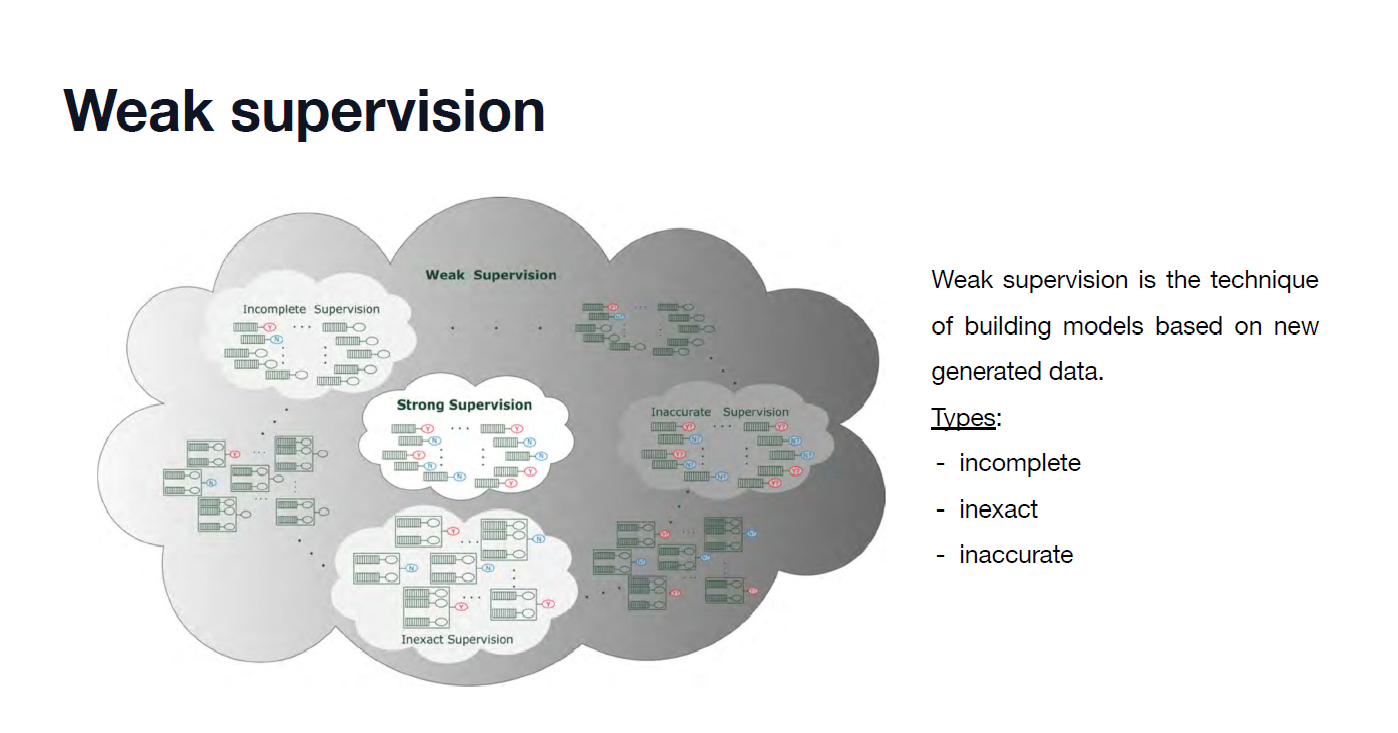
DenseNet, SqueezeNet, MobileNet 이해하기
INTRO ✨
글에 들어가기 앞서 ResNet에 대한 완벽한 이해가 수반됐다는 전제를 알린다.
DenseNet (2016) 👀

- H() 함수: BN, ReLU, 3x3 conv

ResNet
Residual connection을 사용하여, function 이전 값을identity mapping을 통해 더해준다.
DenseNet
- 이전 레이어를 모든 다음 레이어에 직접적으로 연결 \(\rightarrow\) 정보 흐름(information flow)향상.
Residual connection을 사용하여, function 이전 레이어 값들을 모두 concatenate하여 bottlenect 레이어 뒤 기존 불필요한1x1 conv 확장대신 직접 차원을 증가시킨다.- Concat하여 늘어나는 정도를 growth rate(k)로 조절한다.
- Growth rate는 각 레이어가 전체에 어느 정도 기여를 할지 결정한다.
Pre-activation

Pre-activation을 고려하는 이유는 원래의 ResNet에 있는 ReLU가 진정한 identity mapping 개념을 방해하기 때문에 ReLU 순서를 바꿀 수 있는지 확인하기 위함이다.
Weight/Activation/Batch Normalization의 순서 관련한 문제이다.
- Original: Weight 먼저
- Pre-activation: BatchNorm 먼저
BatchNorm \(\rightarrow\) ReLU \(\rightarrow\) Convolution.
Bottle Nect Architecture

마찬가지로 1x1 conv (= bottle neck 구조)를 사용하여 dimension을 reduction한 뒤 output들을 concatenate한다.
Experiment

SqueezeNet (2016) 🎄

Fire Module
하이퍼 피라미터:
s1x1: squeeze layer에서 1x1 filter 수e1x1: expand layer에서 1x1 filter 수e3x3: expand layer에서 3x3 filter 수
(1) Squeeze Layer
GOAL: 3x3 filter로 입력되는 입력 채널의 수를 감소시킨다.
- 3x3 filter의 conv layer 연산량은 \((입력 채널) \times (필터 수) \times (필터 크기)\).
- 하여 입력 채널을 감소하면 3x3 filter 연산량 감소.
s1x1< (e1x1+e3x3)로 설정하여 squeeze layer의 channel수가 expand layer의 channel수보다 작게 설정
1x1 conv layer를 사용하여 channel reduction (원하는 채널 수로 줄이기)
1x1 filter들의 출력값은 하나로 합쳐져서 expand로 전달된다.
(2) Expansion Layer
1x1 conv layer와 3x3 conv layer 함께 병렬 사용
Padding을 사용하여, 두 layer의 output size가 서로 일치하도록 맞춰준다
(3) Squeeze Ratio (SR)

SR은 Expand layer 앞에 있는 squeeze layer의 filter 수를 결정한다.
- Expand layer의 filter에 대한 비율이다.
가령, SR = 0.75이고 expand layer의 필터 개수가 4개라면, squeeze layer 개수는 3개이다.

Bypass

- single bypass: 기존 ResNet
- complex bypass: 입력 채널수와 출력 채널수가 다른 경우, conv 1x1 추가로 채널수 조정 (해당 문장 이해가 어렵다면, ResNet Identity Mapping에 대한 이해를 먼저 하고오면 좋다).
결과적으로 single bypass가 조금 더 나은 성능을 보인다.
bottleneck 문제
squeeze layer의 파라미터 수는 expand layer보다 작아서, 적은 양의 정보가 squeeze layer를 통과한다고 생각한다. 이러한 차원 감소는 모델을 가볍게 해주지만 정보 손실을 유발하므로, bypass를 추가하여 정보 손실을 막는다.
Experinment

MobileNet (2017) 🌷


경량화 모델의 대표적인 알고리즘으로, Depthwise Convolution과 1x1 conv이 특징이다.
Depthwise/Pointwise Convolution
Mobile Net은 두 유형의 합성곱을 함께 사용한다.


Depthwise Convolution
\(D_k^2 \times D_F^2 \times M\ (D_K:\ input\ size,\ M:\ \#\ input\ channel, D_F:\ feature\ map\ size)\)
- 각 channel 별 정보만을 이용하여 convolution 수행
- 필요한 parameter 수 획기적 감소
Pointwise Convolution (= 1x1 conv)
\(N \times D_F^2 \times M\ (N:\ \#\ output\ channel,\ M:\ \#\ input\ channel, D_F:\ feature\ map\ size)\)
- channel 간 weighted sum
- dimension reduction의 효과
Multiplier
Width Multiplier (\(\alpha\))
- 네트워크의 width를 결정하는 파라미터
- conv net에서 width는 각 레이어에서 필터수를 의미
- 각 layer의 input & output channel의 크기를 α 비율만큼 조절
- 입력 채널과 출력 채널에 적용: \(\alphaM,\ \alphaN\).
Depth Multiplier (\(\rho\))

- input resolution(해상도)를 결정하는 파라미터
- 모델의 연산량을 감소시키기 위해 사용
- ρ는 입력 이미지에 적용하여 해상도를 낮춤
Experiment





댓글남기기