DBMS: 데이터 저장 Disks and Files
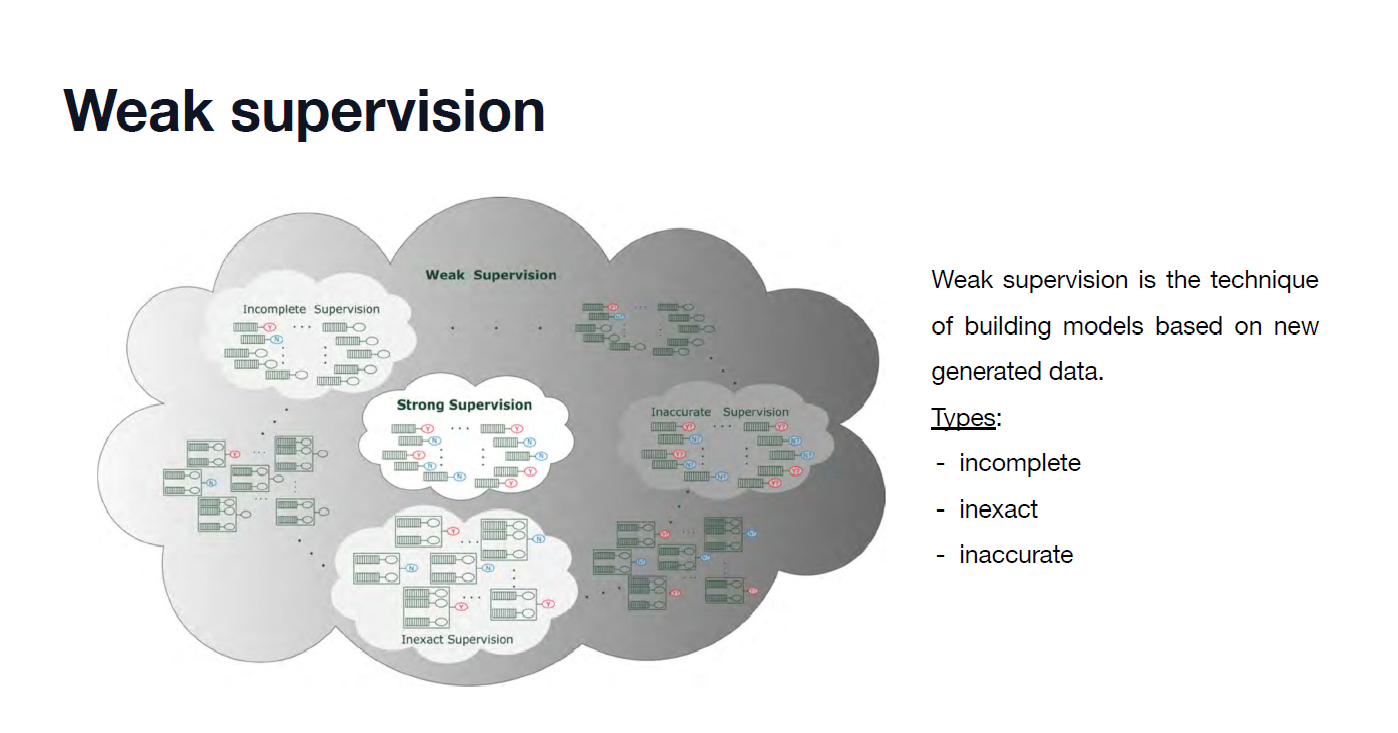
INTRO 🙌
저번 시간에는 SQL에 대하여 알아보았다.
Select eid, ename
From Employees
Where salary > 100K
상기 SQL 문을 입력하면, 시스템은 Employees 테이블을 스캔(scan)한다.
- considers each tuple
- if salary > 100K, then return eid, ename
이번 시간에는 상기 과정이 백앤드(back-end)에서 어떻게 일어나는 것인지, 그리고 Disk, Files, Buffer Manager 세 가지 개념에 대해 알아보자.
Background Knowledge
- 테이블은 file 형태로 disk에 저장된다
- 파일은 다수의 pages를 갖는다.
- 각 페이지는 다수 tuples(rows)를 갖는다.
- 시스템(RDBMS)은 메모리(buffer)에서 한 번에 한 페이지를 처리한다.
Layer Architecture (DBMS) 📌

상기 모형은:
concurrency control(동시성)과 recovery components(복구)를 포함하지 않는다. 가능한 아키텍쳐 중 하나의 형태이다; 각 시스템은 약간 다른 형태를 가지고 있다.
아래 SQL 문을 입력하면 back-end(상기 모형의 각 단계)에서 어떤 처리가 일어나는지 알아보자.
Select eid, ename
From Employees
Where salary > 100K

1. Query Optimization and Execution
- 데이터 찾기: scan through entire table to look at certain appropriate data
- 데이터 뽑기: indexing
2. Relational Operators

3. Files and Access Methods
Disk block 접근 시간(read/write):
- seek time: track 이동 시간(moving arms to position disk head on track)
- varies from about 1 to 20msec
- rotational delay: 한 track에서 desired position까지 회전 시간(waiting for block to rotate under head)
- varies from 0 to 10msec
- transfer time: do reads/writes(actually moving data to/from disk surface)
- about 1msec per 4KB page
Key to lower I/O cost: reduce seek/rotation delays!
Reading pages from disk, writing to pages on disk = very expensive
try to minimize this if we can
4. Buffer Management
Request READ

- request buffer_tag to the buffer manager.
- returns buffer_ID of the slot that stores the requested page.
- If no requested page found in the buffer pool, then loads the page from disk to one of the buffer pool slots
- then, returns buffer_ID’s slot.
- Accesses buffer_ID’s slot (to read the desired page).
Replacement

- 데이터는 RAM 안에 위치해야 실행 가능
- Table에서 데이터 저장 형태: <frame#, pageid> pairs
Replacement 절차
- 만약 요청된 페이지가 pool 안에 존재하지 않을 경우:
- Replacement 위한 frame 선택
- pin count = 0 만족하는 page가 replacement 후보
- If frame is *dirty, write it to disk
- 요청한 페이지를 선택한 frame으로 불러오기
- Replacement 위한 frame 선택
- 페이지 고정(Pin) 및 해당 address 이동
- 완료 이후, 페이지 요청자는 해당 페이지 release 해야함
- unpin it
- dirty 상태로 만들어서 페이지 수정 여부 기록
- 새로운 페이지 요청 들어올 경우, 상기 과정 반복
dirty set
해당 페이지가 memory 존재하지만 disk에 저장된 정보와 다른 경우
LRU (high overhead)
Buffer Replacement Policy
- Frame은 replacement policy에 의거한다 (i.e., Least-recently-used (LRU), Clock, MRU etc.)
- Policy는 각 access pattern에 따라 I/O 개수에 영향을 미친다.
- Sequential flooding: LRU + repeated sequential scans에 의해 발생하는 문제이다.
- Number of buffer frames < # pages in file means each page request causes an I/O.
- LRU 방식으로는 각 요청마다 page miss 발생 (cost ↑)
- MRU를 통해 부분적으로 개선 가능
- Number of buffer frames < # pages in file means each page request causes an I/O.
Sequential flooding
Clock buffer replacement policy

목표: use bit이 cleared된 페이지를 탐색 (=has not been referenced for awhile)

- Keep pointer to last examined page frame
- Traverse pages in circular buffer
- Clear use bits as search
- Stop when find page with already cleared use bit (+ dirty bit cleared), replace this page
use bit = reference bit
5. Disk Space Management
- Lowest layer of DBMS software manages space on disk.
- Higher levels call upon this layer to:
- allocate/delete a page
- read/write a page
Disks 🗂
- 부수적 저장 공간 (Secondary storage device of choice)
- random access vs. sequential access
- 데이터 저장/불러오기는 다음 units을 통해 일어난다: disk blocks or pages.
Disk 구성
[Disk 구조1]

[Disk 구조2]

- The platters spin (say, 90rps).
- Arm assembly는 head 위치를 알맞은 track(desired track)으로 움직인다

- Tracks under heads make a cylinder (imaginary!).
- 하나의 head가 한 번에 하나씩 reads/writes 명령 가능
- Block size는 다수의 sector size 집합체이다.
Files of Records 🗂
- Page, block만으로도 I/O 처리 가능하지만, 고수준 DBMS는 records와 files of records를 필요로 한다.
- FILE: page들의 모음; 각 페이지는 record들의 모음.
- insert/delete/modify record
- 특정 record 일기 (record id 이용)
- 모든 records 스캔 (possibly with some conditions on the records to be retrieved)
Sorted File
Heap File (Unordered Files)
- 가장 간단한 file은 무작위 순서로 records를 보관한다.
- File가 grow/shrink 할수록, disk pages는 allocated/de-allocated 된다.
- record 수준 처리 필요조건:
- File에서 pages 추척하기
- Pages에서 free space 추적하기
- Pages에서 records 추적하기
이 외에도 많은 추적 방법에 대한 대안책이 존재한다.
1. List 방식

- header page id와 Heap file name은 다른 장소에 저장되어 있다.
- 각 페이지는 두 개의 pointers와 data를 갖는다; double linked-list
2. Page Directory 방식

- 한 page의 entry는 해당 page에서 free bytes의 개수를 포함할 수 있다.
- Directory는 page들의 모음이다; linked list 구현은 그저 한 가지 대안책이다.
Page Directory 방식이 모든 HeapFile pages에 대한 linked list 구현보다 더 가볍다/간소하다.
Page Formats
Where and how text, and optionally, page overlays and page segments are to be placed on the page (페이지 단위)
1. Fixed Length Records

Setting a length and storing the records into the file
- Record id = <page id, slot #>
- 페이지에서 Records를 free space로 이동하는 것은 rid를 바꾼다; 따라서, 경우에 따라서 record movement가 불가능하다.
2. Variable Length Records

The records that vary in size
- 페이지에서 Records를 rid 변경 없이 이동 가능하다; fixed-length records에도 적용 가능.
Record Format
How you want data(= record) to be positioned on the logical page (record 단위)
1. Fixed Length

- File의 모든 records에 적용된 field type 정보는 system catalogs에 저장되어 있다.
- i번째 field 탐색은 record 스캔을 필요로하지 않는다; length 고정값이라 바로 위치 계산 가능
- i.e., B+L1+L2
2. Variable Length

can have a different length. Variable-length record
두 번째 옵션(Array of Field Offsets)은 효율적 null 저장 방식을 갖고 있다.
- i번째 field에 직접 접근; small directory overhead
Fixed vs. Variable Length
Variable-length representation
- 장점: Space-efficient
- 단점: Costly record rearrangement is possible
Fixed-length representation
- 장점: Easy implementation of random access
- 단점: Wastes space
System Catalogs

시스템 카탈로그는 데이터베이스 관리자의 도구로, 데이터베이스에 저장되어 있는 모든 데이터 개체들에 대한 정의나 명세에 대한 정보가 수록되어 있는 시스템 테이블이다.
각 index는 structure (e.g., B+ tree)와 search key fields를 가진다
각 relation은 다음을 가진다:
- name, file name, file structure (e.g., heap file)
- attribute name and type, for each attribute
- index name
- integrity constraints
각 view는 view name과 definition를 가진다.
Statistics, authorization, buffer pool size, etc.
- Catalogs들은 relations으로 저장된다.
다음 시간에는 File Organiaztion & Indexing에 대해 알아보자.
Reference
Database Management Systems by Raghu Ramakrishnan and Johannes Gehrke






댓글남기기