[논문 분석] Learning loss for active learning (CVPR 2019)
Learning loss for active learning

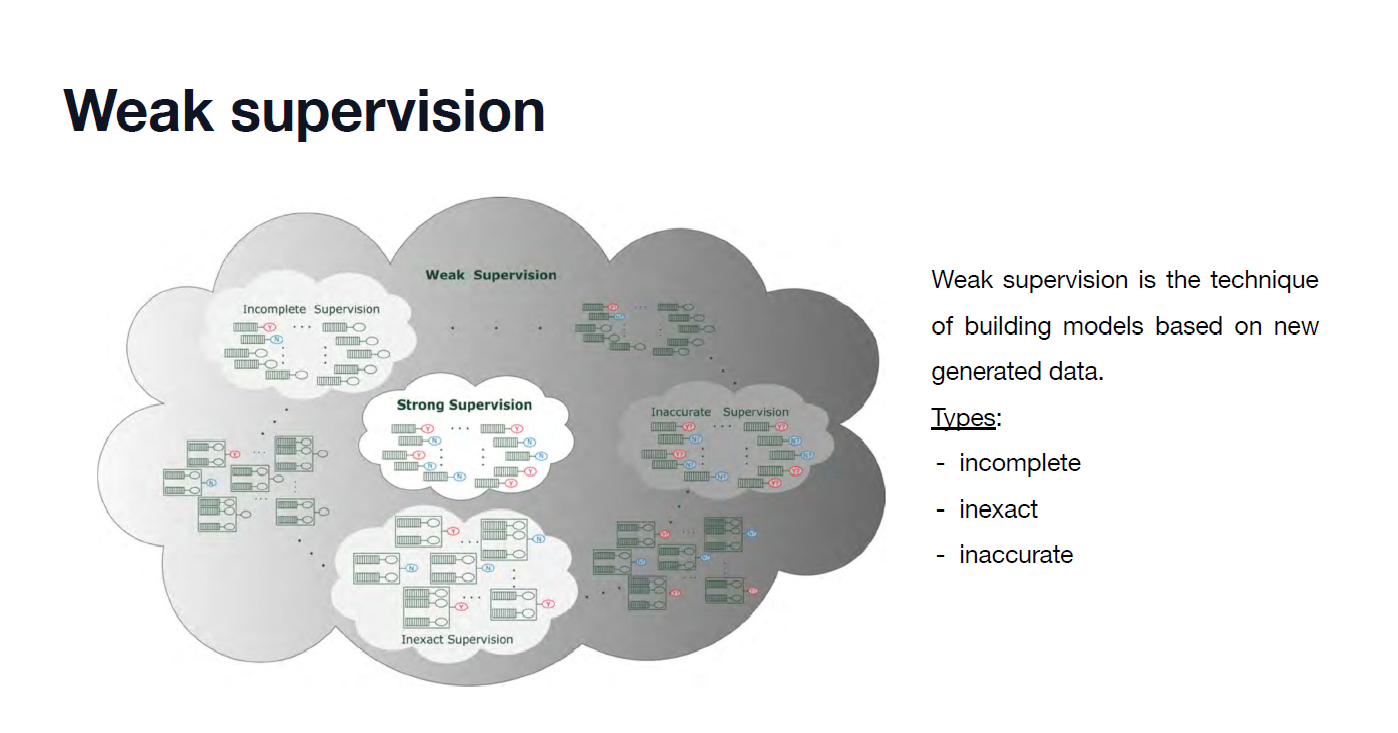
Background
We need big dataset to train a deep learning model

- Low cost: image collection (unlabeled dataset)
- High cost: image annotation (labeled dataset)
Semi-Supervised Learning vs. Active Learning
- Semi-Supervised Learning
- How to train unlabeled dataset based on labeled data
- Active Learning
- What data to be labeled for better performance
Passive Learning

Related Researches
① Least Confident Sampling

② Margin Sampling

③ Entropy Sampling

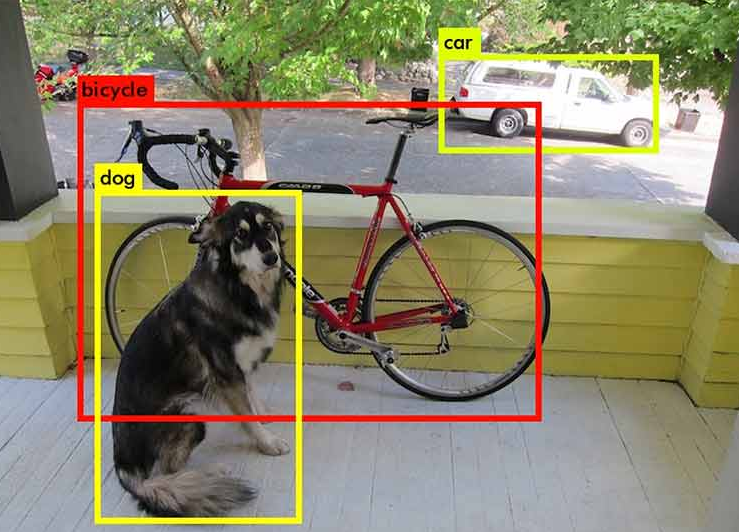
Active Learning

- Using the Welsh corgi image for better performance in training model
Active Learning Process


- Random Sampling
- No observable changes in decision boundary after adding labeled data
- Active Learning
- Training model much faster by selecting unnecessary data near decision boundary
Loss Prediction Module

- Loss prediction for a single unlabeled data
- Smaller network than target model; can be trained under the target model
- No need to define uncertainty through computation
- i.e., Classification, Regression, Object Detection
Loss Prediction: How to Work?

Loss Prediction: Architecture

- GAP: Global Avg. Pooling
- FC: Fully Connected Layers
- ReLU
Method to Learn the Loss

- MSE Loss Function Limitation
- Since target loss decreases, predicted loss is just adapting the change in target loss’s size
Margin Loss


Loss Prediction: Evaluation

Image Classification


Object Detection

Human Pose Estimation


Limitation

Note
referenced by 나동빈




댓글남기기