[논문분석] Saliency as Pseudo-Pixel Supervision for Weakly and Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation (PAMI 2023)
한줄요약 ✔
- Explicit Pseudo-pixel Supervision (EPS++) learns from pixel-level feedback by combining two types of weak supervision: localization and saliency maps.
- localization map ↔ object identity.
- saliency map ↔ rich object boundaries.
- Inconsistent Region Drop (IRD) strategy.
- Effectively handles errors in saliency maps using fewer hyper-parameters than EPS.
- Extended to solve the semi-supervised semantic segmentation problem using image-level weak supervision.
Preliminaries 🍱
CAM
Model Architecture
- CNN의 최종 layer 출력인 feature map에 channel-wise 계산법인 GAP를 적용하여 feature map의 spatial info.를 유지 (기존 CAM에서는 1차원 배열로 point-wise하게 flatten시킨 후 fc-layer의 인풋으로 활용한다).
- 각 채널은 이미지에서 각 객체의 특징을 표현한다 (채널 개수=커널 개수).
- 이후, FC-layer에서 각 특징을 담고있는 feature map의 평균값을 인풋으로 받고, 각 인풋의 각 class에 대한 민감도를 softmax를 거쳐 weights로 표현한다.
Equation
\(Y^c=\Sigma_k w^c_k {1 \over Z} \Sigma_{i,j} A^k_{i,j}\)
- \(Y^c\): class \(c\)에 대한 score (모델 예측 logit/output).
- \({1 \over Z} \Sigma_{i,j} A^k_{i,j}\): feature map \(k\)의 GAP 값.
- \(Z\): feature map \(k\)에서 pixel 개수.
- \(w^c_k\): feature map \(k\)의 class \(c\)에 대한 민감도.
- \(A^k_{i,j}\): feature map \(k\)의 \(i,j\)에 해당하는 pixel 값.
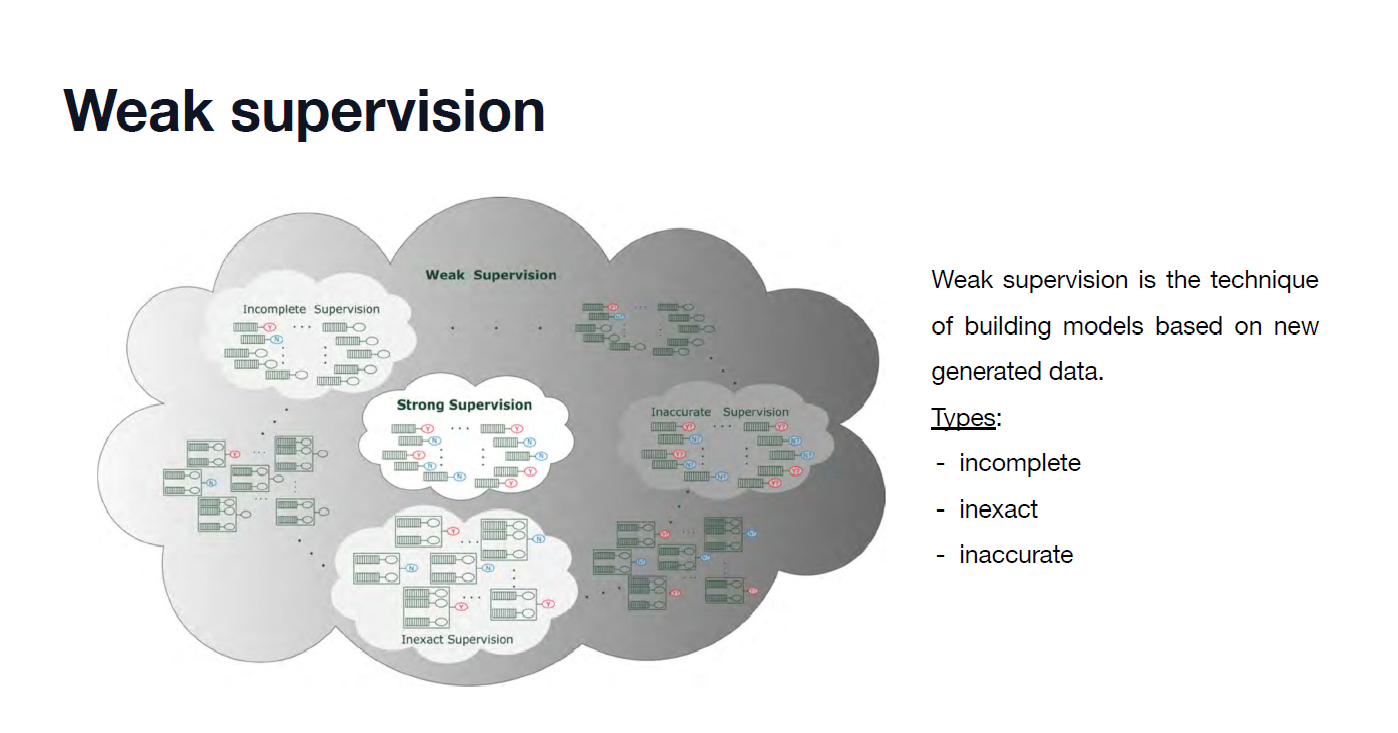
Weak Supervision
1) Weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS)
- Pseudo-masks are generated for target objects using an image classifier (i.e., CAM).
- Then, the segmentation model is trained using the pseudo-masks as supervision.
2) Semi-supervised semantic segmentation (SSSS)
- A segmentation network is trained using a small number of labeled data (e.g., 10% of the original train set) and a large number of \((1)\) weakly labeled data from the pipeline of WSSS or \((2)\) unlabeled data.
- \((1)\) Full supervision (i.e., pixel-level annotation) is partially available, and the rest is weak supervision.
- \((2)\) Full supervision is partially available, and the rest is unsupervised.
⇒ WSSS를 타겟으로 삼는 본 논문에서는 \((1)\)번 경우를 target으로 삼는다.
⇒ 하여 EPS++는 더 정확한 pseudo-masks를 생성하고, 이것은 SSSS의 성능 향상으로 이어진다.
3) Saliency-Guided Semantic Segmentation
- Our EPS++ can be categorized as a saliency-guided method.
- our method utilizes the saliency map as pseudo-pixel feedback for localization maps.
EPS
Challenges and Main Idea💣
C1) DNN-based semantic segmentation methods require a significant amount of pixel-level annotation, which is extremely expensive and time-consuming to obtain.
I1) Weak supervision.
C3) Existing tentative solutions still have their defects in performing semantic segmentation.
I2) EPS++
Problem Definition ❤️
Given a weak dataset \(\mathcal{D}\).
Return a model \(\mathcal{S}\).
Such that \(\mathcal{S}\) approximates the performance of its fully-supervised model \(\mathcal{T}\).
Proposed Method 🧿
Erroneous Saliency Maps
Problems in Saliency Maps
- \((1)\) Missing class error: A saliency map captures the full extent of some target classes, but not all target classes.
- \((2)\) Missing object error: A saliency map covers only a portion of the target object.
- \((3)\) False object coverage error: Non-target region is captured as salient region.
⇒ This systematic error is inevitable because the saliency model learns the statistics of different datasets.
Limitation of EPS
| | \((1)\) | \((2)\) | \((3)\) | | — | — | — | — | | EPS | O | X | X |
- \((1)\): CAM 사용해서 각 클래스 별로 객체 나누는 localization maps 생성 후 다시 취합한다.
- \((2),(3)\): class-wise errors만 해결하고, pixel-wise errors 해결 X \(\rightarrow\)
IRD등장.
Inconsistent Region Drop (IRD)
Background of IRD
- 기존 EPS 한계를 벗어나 pixel level 단위로 handling 하기 위해 도입.
- 정답 saliency map과 estimated foreground saliency map \(M_{fg}\)간의 일치하지 않는
Inconsistent region는 error 모델 성능 저하 요인이라 판단.Inconsistent region: the region where \(M_{fg}\) mismatches the saliency map; it could be erroneous.
- 이러한
Inconsistent region에 해당하는 pixel들은 saliency loss 계산 과정에서 제외.- 하지만, \(M_{fg}\)에는 inaccurate boundaries가 많아서 대부분
inconsistent regions으로 분류되어 saliency loss 가 높게 측정 \(\rightarrow\)Refinement module등장.
- 하지만, \(M_{fg}\)에는 inaccurate boundaries가 많아서 대부분
IRD
- Can preserve boundary information in \(M_{fg}\) and obtain the refined foreground map \(M_r\).
- \(M_r\): refined foreground map obtained by applying
PAMRto the localization maps \(M\).- \(M\): 각 클래스 객체별 localization map; CAM으로 부터 생성됨.
Pixel-adaptive mask refinement (PAMR):
Iteratively refine label predictions by utilizing pixel-level affinity (보다 자세한 내용은 해당 모델 논문 참조).
Architecture
Loss Function
\(\mathcal{L}_{total}=\mathcal{L}_{cls}+\mathcal{L}_{sal}\)
Saliency Loss
\(\mathcal{L}_{sal} = \frac{1}{\vert 1 - N \vert} \Sigma^{HW}_{p=1} (1-N^p) \cdot (M^p_s - M^p_{fg})^2,\)
- \(N=\mathbb{B}(M_r) \odot \mathbb{B}(M_s),\) .
- \(N\): an
inconsistent region.- \(M_r\)과 \(M_s\) 간의
inconsistent region.
- \(M_r\)과 \(M_s\) 간의
- \(M_s\): the saliency map obtained from the off-the-shelf saliency detection model, PFAN trained on the DUTS dataset.
- \(M^p_{fg}\): 기존 EPS으로 생성된 feature map (refined estimated saliency map과 다름).
- \(\odot\): XOR.
- \(\mathbb{B}\): the round operation (i.e., \(\mathbb{B}(M^p_k)=1\) if \(M^p_k >0.5;\mathbb{B}(M^p_k)=0\)).
- \(p\): a pixel.
- \(N\): an
- \(M_{fg}=\Sigma^C_{i=1} y_i \cdot M_{i},\)
- \(C\): class.
- \(y_i \in \mathbb{R}^C\): the binary image-level label.
- \(M_i \in \mathbb{R}^{H \times W}\): the \(i\)th localization map (generated by CAM).
Class Loss
\(\mathcal{L}_{cls}=-\frac{1}{C} \Sigma^C_{i=1} y_i log \sigma (\hat{y}_i)+(1-y_i) log (1-\sigma(\hat{y}_i)),\)
- \(\sigma\): the sigmoid function.
WSSS+SSSS
- Employ the idea of EPS++ on both WSSS and SSSS to demonstrate its effectiveness.
- Apply our EPS++ to the semi-supervised semantic segmentation task (i.e., utilizing both full and weak supervision)
⇒ EPS++ achieves remarkable performances in both weakly and semi-supervised semantic segmentation tasks.
Experiment 👀
- 요즘에 accept되는 논문들은 실험 결과가 거진 좋아서 시간이 허락되지 않으면 굳이 구체적으로 살펴보진 않는다.
- 다만, 경쟁 모델들이 EPP++ 이전 모델인 EPS 모델 논문의 투고 이전 시점의 경쟁 모델들만 활용한 것이 의문이다.
- 보다 자세한 정보는 해당 논문 참조 요망.
Open Reivew 💗
NA
Discussion 🍟
NA
Major Takeaways 😃
NA
Conclusion ✨
- We propose a novel weakly supervised and semi-supervised segmentation framework, namely explicit pseudo-pixel supervision (EPS++).
Reference
NA



댓글남기기